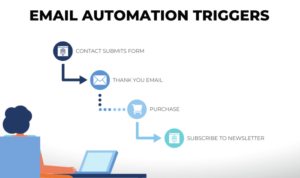
Understanding Customer Segmentation dives into the world of dissecting consumer behavior to revolutionize marketing strategies. From demographic to behavioral segmentation, this topic explores how businesses tailor their approaches to reach the right audience.
Introduction to Customer Segmentation: Understanding Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing customers into groups based on certain characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, or preferences. This practice is crucial in marketing as it allows businesses to better understand their customers and tailor their strategies to meet their specific needs.
Effectively segmenting customers can provide a range of benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved targeting: By dividing customers into segments, businesses can target their marketing efforts more efficiently, reaching the right audience with the right message.
- Enhanced personalization: Segmentation enables businesses to deliver personalized experiences to customers, increasing engagement and loyalty.
- Increased profitability: By understanding the different needs and behaviors of customer segments, businesses can optimize their product offerings and pricing strategies to maximize profitability.
Examples of Customer Segmentation in Action
Companies across various industries utilize customer segmentation to tailor their marketing strategies. Some common examples include:
- Online retailers segmenting customers based on past purchase behavior to send targeted promotions and recommendations.
- Mobile phone providers segmenting customers by usage patterns to offer customized service plans and incentives.
- Automobile manufacturers targeting different customer segments with specific models and features to meet diverse preferences.
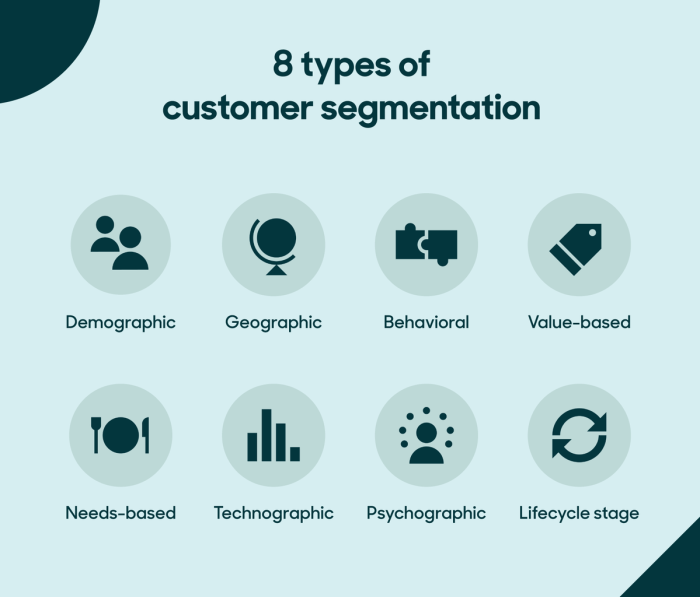
Types of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is a crucial aspect of marketing strategy that involves dividing customers into groups based on similar characteristics. There are various types of customer segmentation that companies utilize to better understand customer behavior and preferences.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation involves dividing customers based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, and family status. This type of segmentation helps companies tailor their products and marketing messages to specific demographic groups. For example, companies like Coca-Cola use demographic segmentation to target different age groups with specific advertising campaigns.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation categorizes customers based on their lifestyle, personality traits, values, attitudes, interests, and behaviors. This type of segmentation provides insights into customers’ motivations and buying behaviors. A company like Apple uses psychographic segmentation to target tech-savvy individuals who value innovation and design in their products.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation divides customers based on their purchasing behavior, usage patterns, brand loyalty, and benefits sought. This type of segmentation helps companies understand customers’ buying habits and preferences. For instance, Amazon uses behavioral segmentation to recommend products based on customers’ past purchases and browsing history.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation involves categorizing customers based on their location, such as country, region, city, or climate. This type of segmentation helps companies customize their offerings to suit the needs and preferences of customers in specific geographic areas. McDonald’s uses geographic segmentation to offer regional menu items based on local tastes and preferences.
Factors Influencing Customer Segmentation
When it comes to customer segmentation, several key factors play a crucial role in how companies target their audience and personalize their marketing strategies. Factors such as age, income, lifestyle, and purchasing behavior significantly influence the segmentation process.
Age
Age is a fundamental factor in customer segmentation as different age groups have varying preferences, behaviors, and needs. Companies often create tailored marketing campaigns based on the age of their target audience to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Income
Income level is another essential factor that influences customer segmentation. Customers with different income levels have distinct purchasing power and preferences, allowing companies to customize their offerings based on affordability and value perception.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle choices, such as hobbies, interests, and values, play a significant role in customer segmentation. Companies leverage lifestyle data to create targeted messaging that resonates with specific consumer groups, fostering a deeper connection with their brand.
Purchasing Behavior
Understanding the purchasing behavior of customers is crucial for effective segmentation. By analyzing buying patterns, frequency of purchases, and preferred products or services, companies can tailor their marketing strategies to meet the unique needs of different customer segments.
Examples of Successful Customer Segmentation Strategies, Understanding Customer Segmentation
One notable example of successful customer segmentation is Amazon’s personalized recommendation system. By analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior, Amazon delivers targeted product recommendations that cater to individual preferences, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
Another example is Starbucks’ loyalty program, which segments customers based on their frequency of visits and purchase preferences. This allows Starbucks to offer personalized rewards and promotions, driving customer loyalty and increasing repeat business.
Methods of Customer Segmentation

Customer segmentation is a crucial strategy for businesses looking to tailor their marketing efforts effectively. Various methods are utilized to categorize customers into distinct groups based on specific criteria. Let’s explore some common methods used for customer segmentation and how they help businesses target their audience more efficiently.
Clustering
Clustering is a method that groups customers based on similarities in behavior, preferences, or demographics. By analyzing patterns and trends within customer data, businesses can identify clusters of customers with similar characteristics. This method helps businesses understand the needs and preferences of different customer groups, allowing for more personalized marketing strategies.
RFM Analysis
RFM analysis stands for Recency, Frequency, Monetary Value, which are three key factors used to segment customers based on their past interactions with the business. This method categorizes customers into segments based on how recently they have made a purchase, how often they make purchases, and how much they spend. RFM analysis helps businesses identify their most valuable customers and target them with tailored marketing campaigns.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future customer behavior. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, businesses can predict which customers are more likely to make a purchase, churn, or engage with marketing campaigns. This method allows businesses to proactively target customers with personalized offers and promotions.
Case Studies
One example of a business effectively applying customer segmentation methods is Amazon. Through its recommendation engine, Amazon uses clustering algorithms to group customers with similar purchase histories and preferences. This allows Amazon to provide personalized product recommendations to each customer, increasing the likelihood of a purchase.
Another example is Starbucks, which uses RFM analysis to segment its customers based on their frequency of visits, amount spent, and loyalty program engagement. Starbucks then tailors its marketing campaigns and promotions to different customer segments, enhancing customer retention and loyalty.
By utilizing methods like clustering, RFM analysis, and predictive modeling, businesses can effectively divide their customer base into distinct groups for targeted marketing efforts, ultimately improving customer engagement and satisfaction.